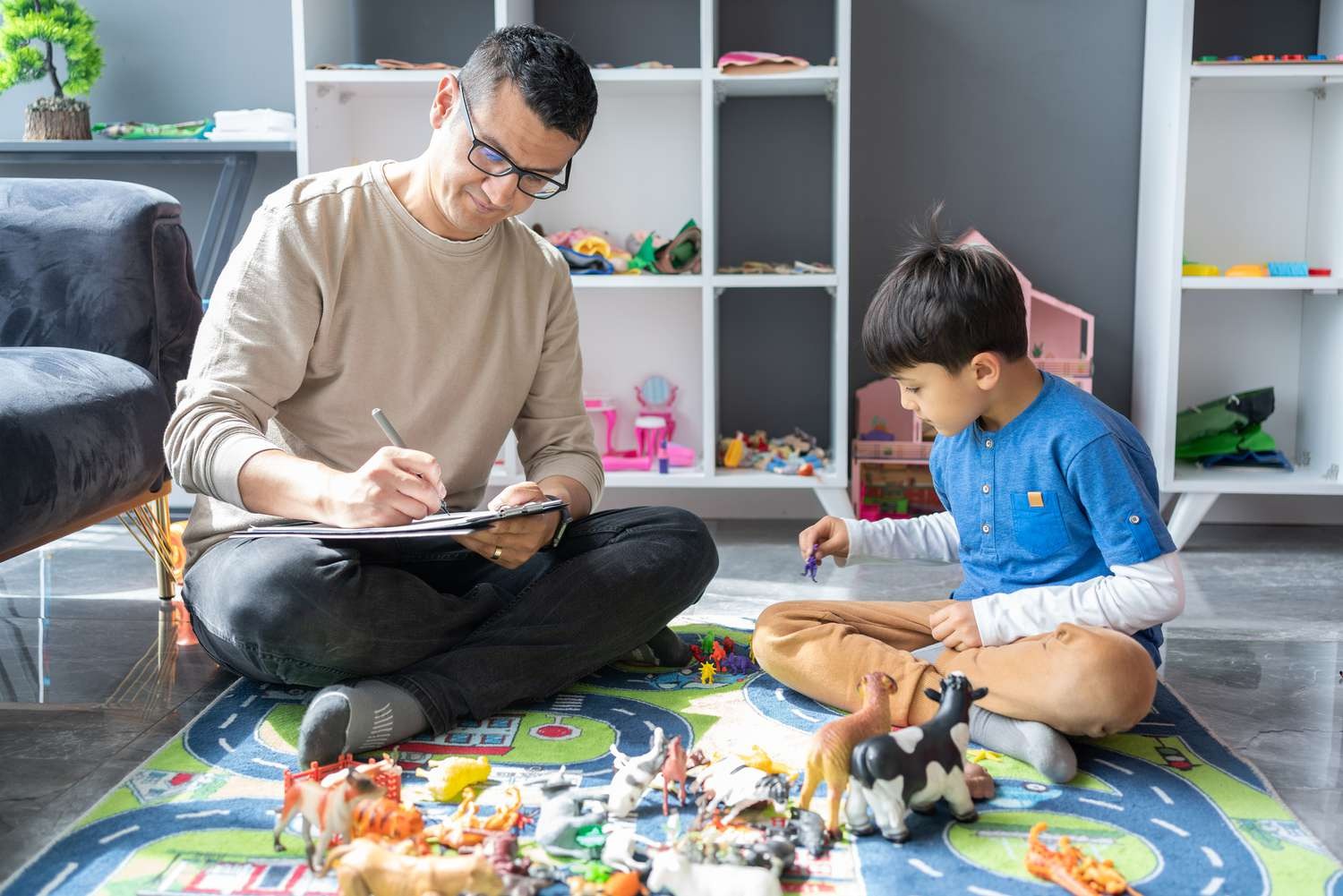
Raising a child comes with many joys, but it can also present challenges, especially when it comes to managing behavioral issues. As a parent, you want to provide the best support possible for your child, but knowing how to address certain behaviors can be difficult. Behavioral therapy is a well-established approach that has proven to be highly effective in helping children with a range of behavioral and emotional challenges. This blog will explore how behavioral therapy for children works, its benefits, and how it can make a positive impact on your child’s life.
Understanding Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative behaviors through positive reinforcement, skill-building, and other evidence-based techniques. Unlike some forms of therapy that focus primarily on understanding the root causes of behavior, behavioral therapy is action-oriented and goal-focused. It aims to modify problematic behaviors by teaching children and their caregivers effective strategies to manage and change these behaviors.
The Principles Behind Behavioral Therapy
The foundation of behavioral therapy lies in the concept of behaviorism, which posits that all behaviors are learned and, therefore, can be unlearned or modified. Behavioral therapy works by identifying the specific behaviors that need to be changed, understanding the factors that reinforce these behaviors, and then developing strategies to encourage positive behavior and reduce or eliminate negative behavior.
Types of Behavioral Therapy
There are several types of behavioral therapy that may be used with children, depending on their specific needs:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT combines behavioral techniques with cognitive therapy to address both thought patterns and behaviors. It’s particularly effective for children dealing with anxiety, depression, and other emotional challenges.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA): ABA is commonly used with children on the autism spectrum and focuses on improving specific behaviors, such as social skills, communication, and academics.
- Parent-Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT): PCIT focuses on improving the parent-child relationship and teaching parents effective ways to manage their child’s behavior.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is used to help children develop coping skills, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness, particularly in children who struggle with intense emotions.
How Behavioral Therapy Works for Children
Behavioral therapy for children is tailored to meet the unique needs of each child. The process typically involves an initial assessment, the development of a treatment plan, regular therapy sessions, and ongoing evaluation and adjustment of the treatment plan as needed.
Initial Assessment and Goal Setting
The first step in behavioral therapy is an initial assessment, where the therapist gathers information about the child’s behavior, emotional state, family dynamics, and any other relevant factors. This assessment helps the therapist identify the specific behaviors that need to be addressed and set clear, measurable goals for the therapy.
Therapy Sessions and Techniques
During therapy sessions, the therapist works with the child and, in many cases, the parents or caregivers. The sessions may involve a variety of techniques, depending on the type of behavioral therapy being used:
- Positive Reinforcement: This involves rewarding the child for displaying positive behaviors. Rewards can be verbal praise, stickers, or other incentives that motivate the child to continue the desired behavior.
- Modeling: The therapist or parent demonstrates positive behaviors that the child is encouraged to imitate. This technique is particularly useful for teaching social skills.
- Skill Building: The therapist may teach the child specific skills, such as problem-solving, emotional regulation, or communication, to help them manage their behavior more effectively.
- Role-Playing: Role-playing allows the child to practice new behaviors in a safe environment, preparing them to use these behaviors in real-life situations.
Parental Involvement
One of the key components of behavioral therapy for children is the involvement of parents or caregivers. Parents are often taught the same techniques that the therapist uses during sessions so that they can reinforce positive behaviors at home. This consistent approach between therapy sessions and the home environment is crucial for the success of the therapy.
The Benefits of Behavioral Therapy for Children
Behavioral therapy offers numerous benefits for children, particularly those struggling with behavioral issues, emotional challenges, or developmental disorders. Below are some of the key advantages of behavioral therapy for children.
Improved Behavior and Emotional Regulation
One of the most significant benefits of behavioral therapy is its effectiveness in improving behavior and emotional regulation. Children who participate in behavioral therapy often show a reduction in problematic behaviors, such as aggression, defiance, or tantrums. They also develop better emotional regulation skills, allowing them to manage their feelings in a healthier way.
Enhanced Social Skills
Behavioral therapy can help children develop essential social skills, such as sharing, taking turns, and understanding social cues. These skills are crucial for forming positive relationships with peers and adults, and they contribute to the child’s overall social and emotional development.
Increased Self-Esteem and Confidence
As children learn to manage their behavior and emotions more effectively, they often experience an increase in self-esteem and confidence. Successfully achieving goals in therapy can give children a sense of accomplishment, helping them to feel more capable and empowered.
Better Parent-Child Relationships
Behavioral therapy often leads to improved relationships between children and their parents or caregivers. By learning how to manage their child’s behavior more effectively, parents can reduce conflicts and build a stronger, more positive bond with their child. This improved relationship can have a lasting impact on the child’s development and well-being.
Common Issues Addressed by Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is versatile and can be used to address a wide range of issues that children may face. Below are some of the most common problems that behavioral therapy can help with.
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder)
Children with ADHD often struggle with impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention, which can affect their performance in school and their relationships with others. Behavioral therapy for children with ADHD focuses on teaching self-control, organizational skills, and strategies for managing impulsive behavior.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
For children on the autism spectrum, behavioral therapy, particularly ABA, can be highly effective in improving communication, social interaction, and daily living skills. Therapy can be tailored to the child’s individual needs, helping them develop the skills necessary to thrive in various settings.
Anxiety and Depression
Children who experience anxiety or depression can benefit from behavioral therapy, especially CBT. This type of therapy helps children identify and challenge negative thought patterns, develop coping strategies, and engage in positive behaviors that improve their mood and reduce anxiety.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
Behavioral therapy is often used to treat children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD), a condition characterized by frequent temper tantrums, defiance, and hostile behavior toward authority figures. Through therapy, children with ODD can learn to manage their anger, follow rules, and improve their relationships with parents and teachers.
Is Behavioral Therapy Right for Your Child?
Deciding whether behavioral therapy is the right approach for your child can be challenging. It’s important to consider your child’s specific needs, the severity of their behavioral issues, and your willingness to be involved in the therapy process.
Signs That Your Child May Benefit from Behavioral Therapy
If your child is exhibiting any of the following signs, behavioral therapy may be a good option:
- Frequent temper tantrums or meltdowns
- Difficulty following rules or instructions
- Struggles with social interactions or making friends
- Persistent anxiety, sadness, or mood swings
- Problems with attention, focus, or impulse control
Consulting with a Professional
Before starting behavioral therapy, it’s essential to consult with a licensed therapist or psychologist who specializes in working with children. They can assess your child’s needs and recommend the most appropriate type of therapy. It’s also important to choose a therapist who has experience and training in the specific techniques that will be used in therapy.
Conclusion
Behavioral therapy for children is a powerful tool that can help address a wide range of behavioral and emotional challenges. By focusing on changing negative behaviors and reinforcing positive ones, this type of therapy can lead to significant improvements in a child’s behavior, social skills, emotional regulation, and overall well-being.
If you’re concerned about your child’s behavior or emotional health, consider exploring behavioral therapy as a potential solution. With the right approach and the involvement of a skilled therapist, your child can learn to overcome their challenges and thrive in all areas of their life. Whether your child is dealing with ADHD, anxiety, autism, or other behavioral issues, behavioral therapy offers a structured, evidence-based approach that can make a lasting difference in their development and happiness.
Keep an eye for more news & updates on Discover Tribune!