Key Takeaways
- A comprehensive look at mRNA technology and its significance in modern medicine.
- An overview of the revolutionary advancements in vaccines and therapeutics.
- A discussion on the challenges and ethical debates surrounding mRNA technology.
- Real-world applications and insights into the prospects of this technology.
Introduction
In recent years, mRNA products have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, promising to revolutionize how we approach medicine and biotechnology. This cutting-edge technology, which harnesses the potential of messenger RNA, is reshaping vaccine development and therapeutic solutions globally.
Exploring the intriguing realm of mRNA reveals its significant influence on healthcare and the obstacles and moral dilemmas it brings. Investigating the intricacies of mRNA technology uncovers a vibrant space where science, creativity, and compassion come together to meet current healthcare demands.
This article will investigate the present status of mRNA technology, analyzing its uses, challenges, and future possibilities. By understanding its revolutionary promise and realities, we can appreciate its role in modern science. The journey of mRNA technology is one of significant promise and intricate challenges, symbolizing scientific innovation and the quest for better health outcomes.
Understanding mRNA Technology
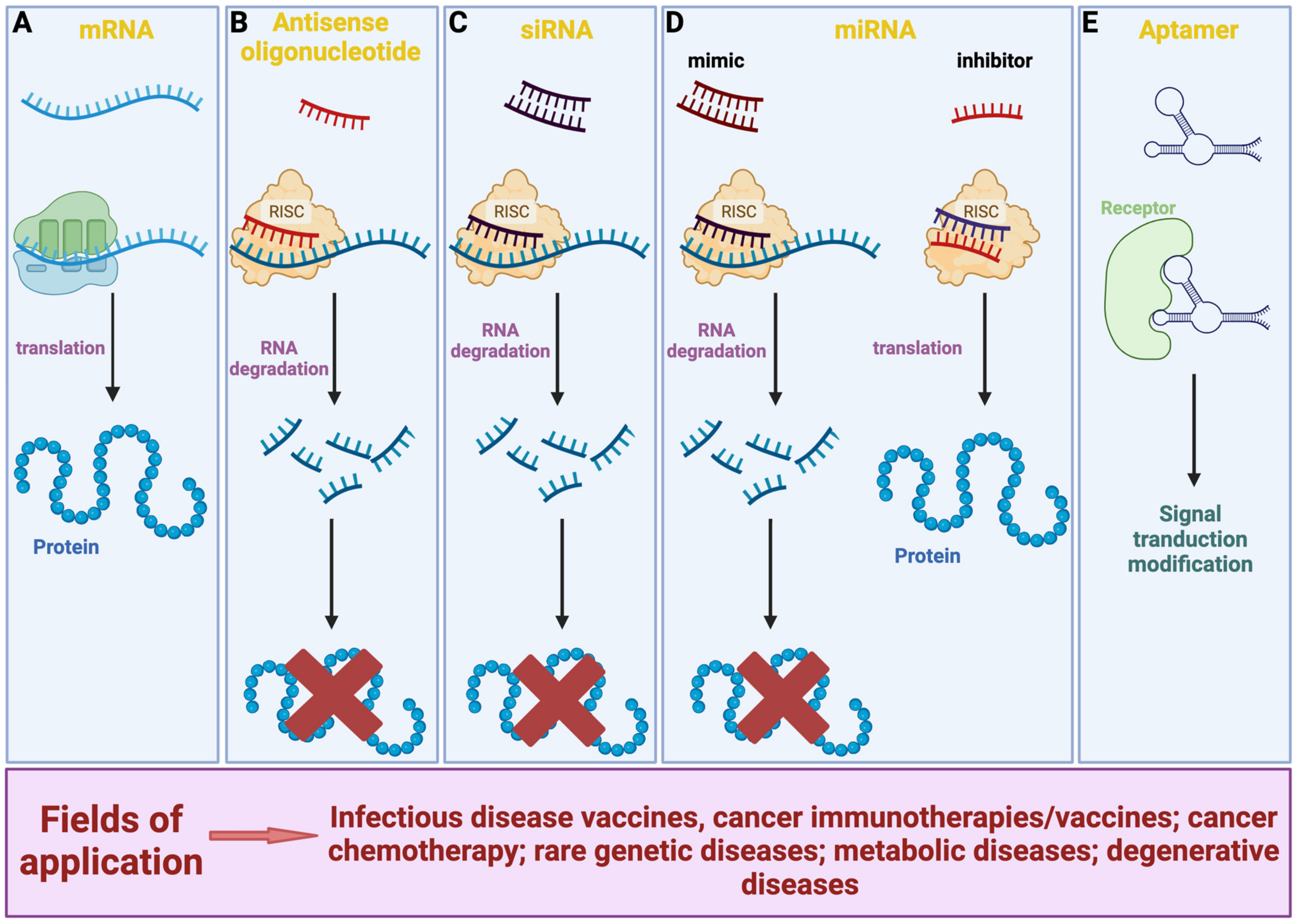
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a vital component of our biological machinery. It serves as the blueprint for protein synthesis and acts as a crucial link between the DNA in our cells and the ribosomes, where proteins are made. It carries the genetic instructions necessary to produce proteins, which perform many functions within our bodies. Though the study of mRNA dates back several decades, its application in developing vaccines and treatments has only recently gained momentum.
Exploration of the molecular complexities of mRNA has paved the way for novel approaches in genetic medicine, representing a significant advancement in the treatment and prevention of diseases.
The Revolution in Medicine
The forefront of medical innovation, especially in vaccine development, is currently occupied by mRNA technology. The swift creation of COVID-19 vaccines demonstrated the remarkable potential of mRNA in combating infectious diseases, offering a rapid response during a global health crisis. Besides vaccines, mRNA is promising for personalized medicine and cancer treatments, aiming to tailor drugs to individual genetic profiles and provide more effective and targeted therapies. This customization reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions and increases treatment efficacy, positioning mRNA as a cornerstone of futuristic medicine that adapts to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
How mRNA Technology Transforms Therapeutics
The ability to design mRNA sequences that instruct cells to produce specific proteins opens new avenues for treating various conditions. This precision not only enhances efficacy but also reduces the risk of adverse side effects, which is a significant improvement over traditional methods. By programming cells to synthesize therapeutic proteins that combat diseases at a molecular level, mRNA technology offers hope in treating conditions previously deemed untreatable or difficult to manage. The ripple effect of this innovation is seen in the potential for addressing chronic illnesses and complex genetic disorders, fundamentally altering the therapeutic landscape.
Challenges in mRNA Technology
Despite its impressive achievements, mRNA technology faces several hurdles. Manufacturing mRNA products at scale is complex and demands rigorous quality control to ensure consistent and effective outputs. Additionally, these products require ultra-cold storage, which complicates distribution efforts, especially in developing regions lacking infrastructure. These logistical challenges highlight the need for advancements in storage technology and global distribution networks to realize the full potential of mRNA’s promise. Furthermore, exploring potential risks and side effects, such as unintended immune responses, must be carefully monitored. According to Nature, ongoing research is vital to understanding and mitigating these risks, thereby ensuring the safe deployment of mRNA therapeutics in varied populations and environments.
Ethical Considerations
The rapid adoption of mRNA technology invites ethical scrutiny. Concerns about genetic manipulation and privacy persist, highlighting the need for robust regulations to guide its development. These debates underscore the importance of balancing innovation with ethical responsibility, ensuring that mRNA advancements benefit society without compromising individual rights and public trust. With the progress of technology, regulatory frameworks must evolve to ensure transparency and public involvement. This is necessary to handle ethical challenges and establish trust in the transformative power of mRNA in healthcare.
Real-Life Applications
mRNA technology is not confined to theoretical potential; it is already making tangible impacts. Vaccines against infectious diseases are the most visible application due to their critical role in public health. Still, ongoing trials explore its capabilities in treating rare genetic disorders and chronic conditions like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy. The adaptability and precision of mRNA technology allow for rapid innovation, potentially addressing diverse healthcare needs with unprecedented accuracy. Insights, such as those from the National Library of Medicine, offer a glimpse into the future of mRNA, suggesting that its applications might soon extend to neurodegenerative diseases and beyond, ushering in an era of medical solutions tailored to intricate biological challenges.
Looking Ahead: The Future Potential
The future of mRNA technology is bright, with researchers actively exploring improvements in delivery mechanisms and stability. These advancements could significantly broaden the scope of mRNA treatments, potentially transforming global health paradigms by enhancing accessibility and effectiveness. As our science knowledge becomes more advanced, exploring new uses could result in significant advancements in treating infectious diseases, genetic disorders, and certain types of cancer. This growing promise showcases mRNA technology as a critical participant in the continued development of healthcare, ready to surpass existing limitations and introduce fresh opportunities for global health and well-being.
Conclusion: mRNA’s Continuing Journey
As we navigate the frontier of mRNA technology, it is crucial to remain mindful of its immense promise and complex challenges. By embracing cutting-edge research and maintaining ethical vigilance, we can pave the way for mRNA to fulfill its potential to enhance human health. This Journey requires a concerted effort from scientists, policymakers, and healthcare practitioners to harness the full power of mRNA while responsibly addressing the ethical and logistical hurdles accompanying such transformative technology. The ongoing collaboration between diverse stakeholders will be the catalyst for unlocking mRNA’s potential to shape a healthier future for all.